Call option — what is it?
Options are divided into two main types — call and put. Both have different meanings and applications and can apply to both standard and binary options. A call option is a very popular instrument on the financial market. Traders (market participants who strive for and earn profit not from the fact of buying or selling, but from the trading process itself) most often use call options when working in the options market.
General concept of a call option
 A call option is a type of security that gives its buyer the right, but not the obligation, to purchase the underlying asset at an agreed price. The option has its own term, after which the holder loses this right.
A call option is a type of security that gives its buyer the right, but not the obligation, to purchase the underlying asset at an agreed price. The option has its own term, after which the holder loses this right.
The seller is obliged, within the specified period, to sell the underlying asset to the option holder at his first request. During the term of the contract, the price of the subject of the deal may rise sharply or, on the contrary, fall. Regardless of such fluctuations, the seller must sell the asset at the agreed (strike) price. If the market value has risen significantly, the difference is compensated at the seller’s expense. He assumes this risk in exchange for a one-time payment received at the moment of the deal — the option premium.
Types of call assets
Depending on which asset serves as the central part of the deal, options can be divided into several types.
Commodity call options
The subject of the deal is a commodity, whether food products or goods of light or heavy industry. A commodity call option is essentially a company’s initial shares, except for dividends received by shareholders: the option can be exercised only once. Young companies issue this type of security, under which they undertake to sell their products at a price below the market average in exchange for a premium that they can spend on opening and developing their business.
Exchange-traded call options
This type of security began to develop later, but soon became very popular. Both parties to the agreement found very advantageous aspects for themselves. The seller earns profit from premiums. With a large number of deals, such income can easily cover expenses related to the difference between the option’s strike price and the market price of the asset in case of an unfavorable outcome. The buyer seeks income from fluctuations in the asset’s value.
Gradually, the asset itself disappeared from the deal between buyer and seller, since both pursued one goal — profit, and the object of the contract was merely a means to achieve it. Options trading began to turn into a financial bet between two parties. It was soon expanded into barrier options, and later transformed into binary options.
Currency call options
On the Forex exchange (the interbank currency market), currency options began to develop. At first, they were used to generate income from possible fluctuations in foreign exchange rates. Their main advantage over ordinary buying and selling is minimal financial risk. In exchange for such security, the trader received slightly lower profits due to the premiums paid to the seller.
Example of using a call option
For example, let us take a currency call option. Due to China’s strengthening position on the international stage, a sharp rise in the national currency rate is possible in the coming months. The yuan may increase by as much as 4–5%, which is considered significant by global standards. The jump will occur only in a few months, and during this time many events may occur that could hinder the rate’s growth, so converting assets into yuan is too risky. A more rational approach is to buy a currency call option to purchase a large amount of yuan at the current exchange rate for up to three months. The option price is 1% of the current value of the Chinese currency. If the forecast is correct and the yuan rises by 4%, the investor will earn 3% of the invested amount (4% growth minus 1% premium paid). If the deal is unsuccessful, he loses only 1% of the funds he intended to invest.
The concept of “call” in binary options
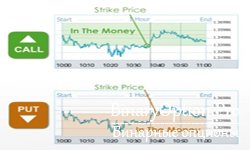 The development of the financial market and options trading has given rise to a new type of digital trading that differs greatly from the traditional concept. Here, the terms call and put no longer mean separate types of options. They indicate the possible direction of the underlying asset’s price.
The development of the financial market and options trading has given rise to a new type of digital trading that differs greatly from the traditional concept. Here, the terms call and put no longer mean separate types of options. They indicate the possible direction of the underlying asset’s price.
Let us take a closer look. Binary options are essentially bets on the behavior of an asset’s price in the near future (minute, hour, day, week). The investor chooses an asset and makes a forecast: whether its price will fall or rise. If he believes the price will rise, he places a Call bet; if it will fall, he places a Put bet.
Thus, in binary trading, a call option is a bet on an increase in the value of the underlying asset. If during the option’s term the asset does indeed rise in price, the bet wins and the investor can earn up to 85% of the investment amount.