What is a put option?
An option is a security that is very popular among traders. By buying or selling options, one can earn a decent profit, but this requires preparing a strategy. It depends on which type of options is used — call or put. For fast trading, calls are used more often; a put option is a more global financial instrument that is frequently used by large companies.
General concept of put options
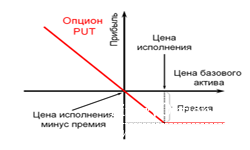 A put option is a security whose holder can sell an asset at an agreed (strike) price regardless of the market condition of that asset. The option seller is obliged to immediately fulfill the requirements of the security holder; if this is not possible, for example in the case of early expiration, the seller must compensate the potential profit of the security holder.
A put option is a security whose holder can sell an asset at an agreed (strike) price regardless of the market condition of that asset. The option seller is obliged to immediately fulfill the requirements of the security holder; if this is not possible, for example in the case of early expiration, the seller must compensate the potential profit of the security holder.
Options are exercised in order to obtain easy profit from fluctuations in the asset’s value and to hedge already made investments.
The advisability of using an option is determined by its profitability. If the underlying asset has significantly depreciated during the term of the contract, a rational decision would be to sell the asset through the option. If the asset, on the contrary, has increased in price, the option can be allowed to expire.
Types of put options
The underlying asset is the main object of an option contract. Depending on what exactly serves as the underlying asset, any type of option can be divided into several more categories.
Commodity put options
This term generally refers to options whose underlying assets are mineral resources, precious metals, gemstones, and so on. In a broader sense, any tangible item can serve as the underlying asset.
Such securities are usually used by companies producing the underlying asset, especially when its production involves a long period between financial investment and payback. Such industries include agriculture, the production of certain food products, alcoholic beverages.
Exchange-traded put options
 A put option is a favorite way of hedging invested funds for many traders. Most often, the underlying asset is shares or other securities.
A put option is a favorite way of hedging invested funds for many traders. Most often, the underlying asset is shares or other securities.
If a price collapse of this asset is expected in the near future, an option is purchased under which one party undertakes to buy it from the other at the current price. In the future, such an option can become a lifeboat for the investor, allowing them to recover at least part of their invested funds in case of market instability.
Currency put options
The most well-known and accessible way to earn from trading is investing in currency for subsequent resale.
Experienced exchange players try to protect themselves as much as possible from financial losses regardless of how confident they are in their forecast. For this purpose, they acquire currency put options, together with which they receive the right to convert currency at the rate valid at the present moment.
Use of put options
It is quite difficult to fully understand what put options are without examples, so it is worth considering situations in which such securities are most popular. As an example, let us take an exchange-traded option.
A large company is about to face serious financial difficulties: several contracts have been lost, and the latest batch of goods sold poorly. This information has not yet been made public, but it is gradually leaking out. With the right skills, such a lead can be turned into a decent profit. This is exactly what traders seek when they acquire currency put options granting the right to sell the company’s shares at the current price.
During the crash, the trader buys shares at a very low price and sells them to the party that sold him the option. As a result of this operation, the trader receives significant profit from the price difference, essentially doing nothing for it.
The concept of “put” in binary options
 Binary options are a type of options in which payment is possible only if the forecast of the underlying asset’s price behavior in the near future is correct. The asset itself leaves circulation, and in the event of a successful outcome, the seller pays the investor only the profit.
Binary options are a type of options in which payment is possible only if the forecast of the underlying asset’s price behavior in the near future is correct. The asset itself leaves circulation, and in the event of a successful outcome, the seller pays the investor only the profit.
This term relates more to digital trading and gradually loses common features with the traditional understanding of options. Even the concepts of “call” and “put” have taken on a different meaning. In binary options, this term denotes not the type of contract, but an action. If an investor believes the price will rise in the near future, they place a “call” bet; if it will fall — a “put”.